Stay Safe in 2026 with These New Year’s Resolutions
We’re approaching the end of 2025, so we encourage you to consider your New Year’s resolutions. For many people, the new year offers an opportunity to reflect on habits we’d like to adopt or solidify. Although we support reducing social media use and making other positive lifestyle changes, we’d like to suggest a few additional resolutions to improve your digital security and reduce the risk of bad things happening to you online.
If you read through this list and think, “I’m already doing all that,” then you’re done. Keep up the good work!
Back Up All Your Devices Regularly
The most important thing you can do to avoid digital disasters is to back up your data regularly. Bad things happen to good devices, like a Mac’s SSD failing, an iPhone falling into a pool, or data being lost due to theft, fire, or flood. With a solid backup plan, you can recover from nearly any problem.
For the Mac, the easiest way to back up is to use an external drive with Time Machine, but an off-site or Internet backup is also essential. Backblaze is a good choice, but there are numerous online backup services. For iPhones and iPads, it’s simplest to back up to iCloud, which automatically happens every night if you turn it on in Settings > Your Name > iCloud > iCloud Backup. You can also back up iPhones and iPads to your Mac if you do not have enough iCloud storage space. Apple Watches automatically back up to their paired iPhones, and that Watch data is included in iPhone backups, making restores straightforward. Whatever your setup, restore a few files periodically as a test to make sure your backups are working.

Always Install Security Updates
An important step to enhance your security is to install new operating system updates and security updates promptly after Apple releases them. While the specifics rarely make headlines because they are highly technical and detailed, you can gauge the significance of security updates by noting that a typical update fixes 10–30 vulnerabilities identified by Apple or external researchers. Other security updates include only one or two fixes, as they’re aimed at addressing zero-day vulnerabilities currently being exploited in the wild.

It’s usually wise to wait a few days after an update appears before installing it, in case it causes any undesirable side effects. Although such problems are rare, when they do happen, Apple quickly pulls the update, resolves the issue, and releases a new version, typically within a few days.
Use a Password Manager
We’ll keep emphasizing the importance of a password manager until passkeys—the replacement for passwords—become widespread, which will take years. Until then, if you’re still typing passwords manually or copying and pasting from a list stored in a file, please start using a password manager like 1Password or Apple’s Passwords, which is now pretty good. A password manager provides six significant benefits:
- It generates strong passwords for you. Password1234 can be hacked in seconds.
- It stores your passwords securely. Anyone walking by your unlocked Mac can read an Excel file on your desktop.
- It enters passwords for you. Wouldn’t that be easier than typing them in?
- It audits existing accounts. How many of your accounts use the same weak password, which has likely been stolen in multiple breaches?
- It lets you access passwords on all your devices. Logging in to websites is just as easy on the iPhone and iPad!
- It can store and enter two-factor authentication codes. Whenever possible, protect important accounts with two-factor authentication so even a stolen password won’t provide access.
A bonus benefit for families is password sharing. It allows couples to share essential passwords or parents and teens to share specific passwords.

Using a password manager is quicker, simpler, and more secure. If you need assistance getting started, reach out.
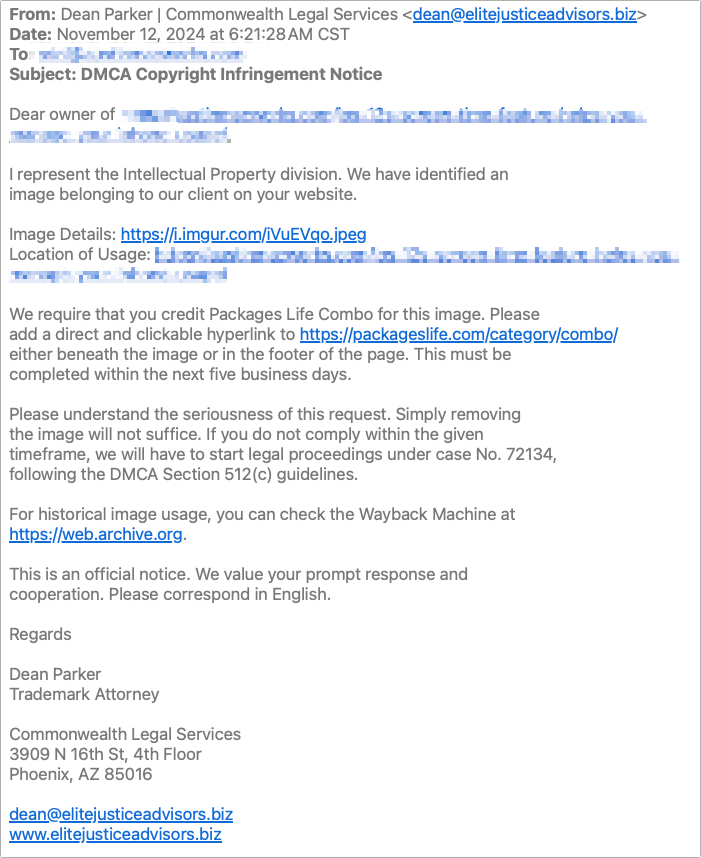
Beware of Phishing Email
Individuals and businesses often experience security breaches due to phishing, which involves fake emails that trick someone into revealing login details, credit card numbers, or other sensitive data. While spam filters catch many of these attacks, you must stay alert. Here’s what to watch out for:
- Any email that tries to get you to reveal information, follow a link, or sign a document
- Messages from unfamiliar people, asking you to take an unusual action
- Direct email from a large company for whom you’re an anonymous customer
- Forged email from a trusted source requesting sensitive information
- Urgent threats like “account locked,” “unauthorized charge,” or “action required”
- All messages that contain numerous spelling and grammatical mistakes

When unsure, avoid clicking the link or replying to the email. Instead, reach out to the sender via another method to verify the message’s authenticity. Legitimate companies—especially Apple, financial institutions, and cellular carriers—will never ask for your password or two‑factor codes by email, text, or voice.
Never Respond to Unsolicited Calls or Texts
Phishing attacks increasingly take place via texts and phone calls—and even some via deepfake audio and video. Because of weaknesses in the telephone system, these messages and calls can appear to come from trusted companies like Apple and Amazon. Other common scams warn about unauthorized logins or payments to trick recipients into calling scammers, advertise fake deliveries with malicious tracking links, or send fake two-factor authentication messages that prompt recipients to click a link to “secure” their account.

Avoid clicking links in texts unless you recognize the sender and it makes sense for you to receive that link. (For example, Apple might send text messages with delivery details for a recently placed order.) Never enter login information on a website you reach through a link because you can’t be sure it’s legitimate. Instead, if you’re interested in more details, go directly to the company’s official website by typing its URL into your browser, then log in from there.
For calls from companies, unless you’re expecting a callback regarding a support ticket you opened, don’t answer—caller ID can be spoofed. Let the call go to voicemail, and if you believe it’s important to respond, look up the company’s phone number from a reliable source and contact someone at that number instead of using the one provided by voicemail.
Avoid Anything Associated with Sketchy Websites
We won’t dwell on this last point, but it’s worth noting that you’re much more likely to encounter malware on fringe websites or those that cater to societal vices. The more you can steer clear of sites that deal with pirated software, cryptocurrency, adult content, gambling, or the sale of illicit substances, the safer you’ll be. That’s not to say reputable sites haven’t been hacked and used to spread malware, but such cases are far less frequent.
Don’t call numbers from pop‑ups or ads, don’t grant remote access, and don’t pay for any service you didn’t seek out unprompted. Instead, go directly to the company’s official site (type the URL) or contact us for help. And never paste commands into Terminal from websites or “verification” pages—you could install malware without realizing it. If you are worried after spending time in the darker corners of the Web, download a free copy of Malwarebytes and manually scan for malware.

Let’s raise a glass to staying safe online in 2026!
(Featured image by iStock.com/Marut Khobtakhob)
Social Media: Kick off 2026 with smart security habits: back up every device, stay current on software updates, outsmart phishing attempts, avoid sketchy sites, and streamline your logins with a password manager.