Have you heard the expression “hit by a bus”? It’s a somewhat macabre attempt to inject a little levity into planning for the unthinkable event of dying without warning. No one expects to be hit by a bus, but people do die unexpectedly in all sorts of ways. That’s terrible, of course, but it’s also incredibly hard on that person’s family, who suddenly must deal with an overwhelming number of details. Many of those details revolve around the deceased’s digital life—devices, accounts, passwords, subscriptions, and more.
We strongly encourage everyone, regardless of age or infirmity, to think about what your family would want and need to do with your digital presence in the event of your death. The ultimate guide to this topic is Joe Kissell’s book Take Control of Your Digital Legacy, although the current version is a little out of date and is slated for updating in 2022.
The next edition of that book will undoubtedly discuss Apple’s new Legacy Contact feature, introduced in iOS 15.2, iPadOS 15.2, and macOS 12.1 Monterey. It enables you to specify one or more people as a Legacy Contact. Should you die unexpectedly, those people can use an access key along with your death certificate to access much of your Apple content and remove Activation Lock from your devices. (If you have time to prepare for your passing, it’s easier to share all your passwords and passcodes explicitly.) The person or people you set as Legacy Contacts don’t have to be running Apple’s latest operating systems or even be Apple users, though it’s easier if they are. (Like so many other things in life.)
Don’t put off specifying someone as a Legacy Contact, whether it’s a family member or close friend. The entire point of the “hit by a bus” scenario is that it’s both unexpected and could happen at any time. (It’s possible to get access without being a Legacy Contact, but it requires a court order and will undoubtedly be significantly more work.)
Apple provides good directions for the Legacy Contact feature, and while we’ll summarize the steps below, read Apple’s documentation to get the word from the horse’s mouth. Apple’s support pages include:
What Data Can a Legacy Contact Access?
Apple has the full list at the link above, but in short, a Legacy Contact can access anything stored in iCloud, including photos, email, contacts, calendars, messages, files, and more, as well as the contents of iCloud Backup. Not included are licensed media (music, movies, and books), in-app purchases (upgrades, subscriptions, and game currency), payment information (Apple ID payment info or Apple Pay cards), and anything stored in the account holder’s keychain (usernames and passwords, credit card details, and more). A Legacy Contact cannot access the deceased’s devices—Apple is incapable of sharing passcodes. However, Apple can remove Activation Lock so those devices can be erased and reused.
How Do You Add a Legacy Contact?
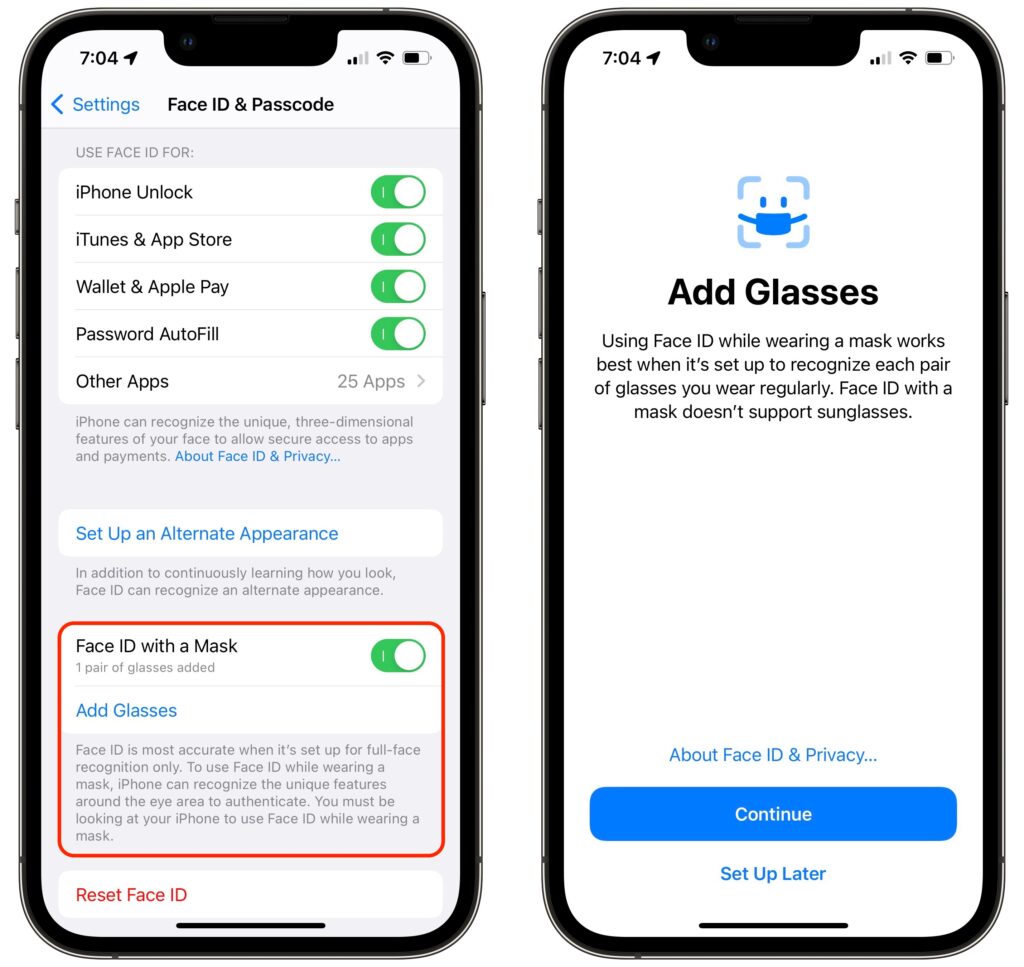
Adding someone as a Legacy Contact is easy. You must be running iOS 15.2, iPadOS 15.2, or macOS 12.1 Monterey to initiate the process, and two-factor authentication must be turned on for your Apple ID (this is a very good idea anyway).
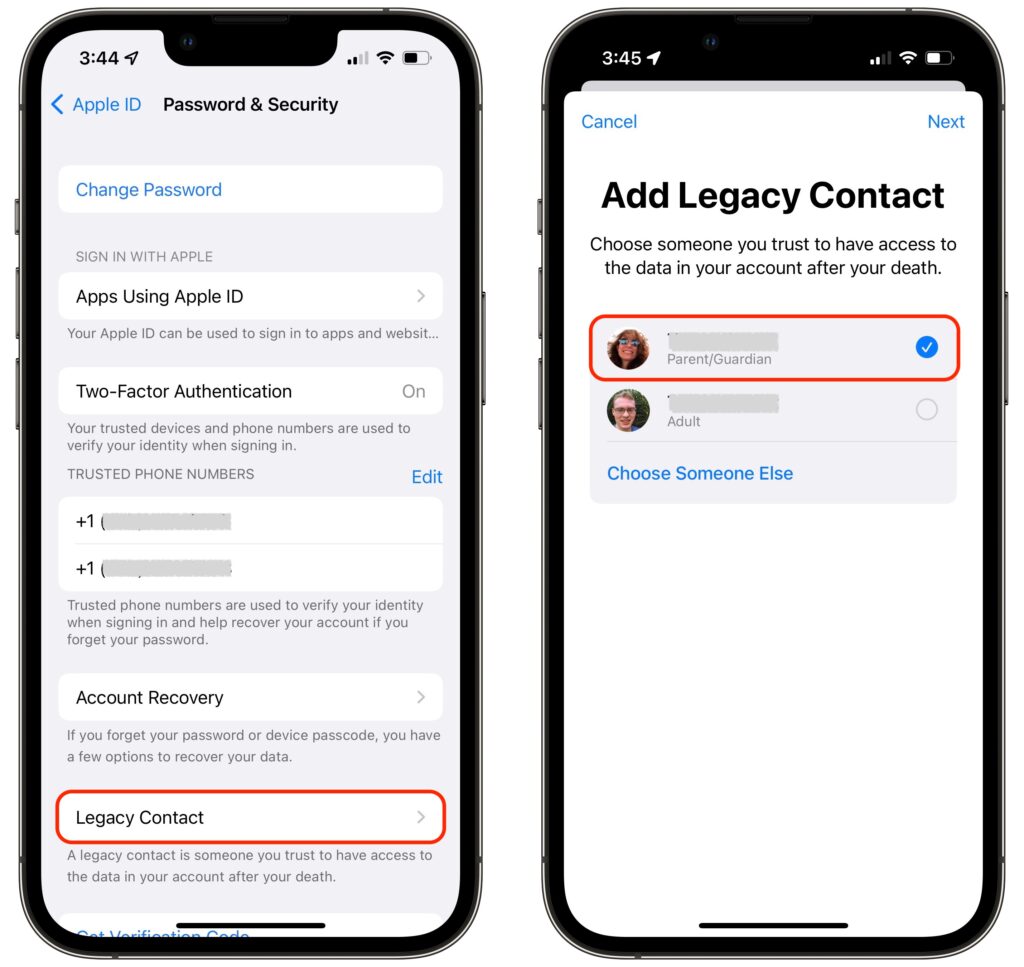
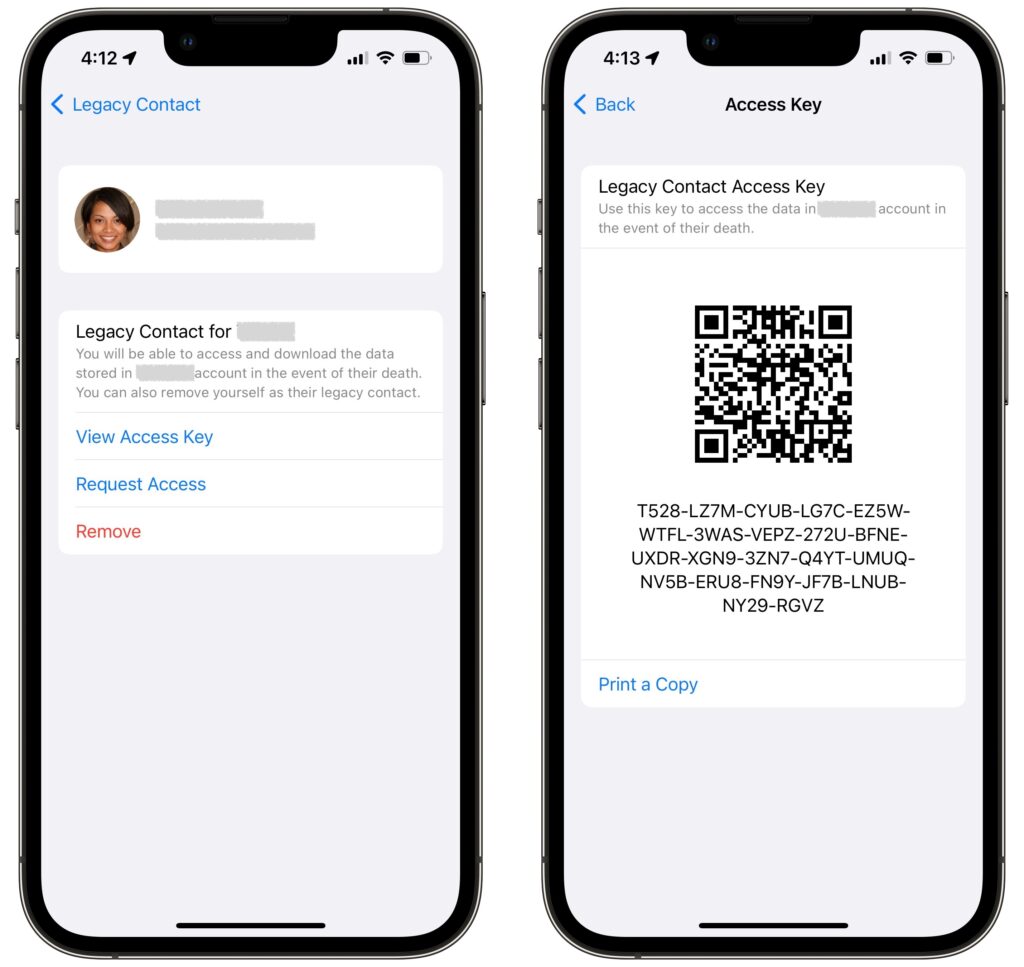
On an iPhone or iPad, go to Settings > Your Name > Password & Security > Legacy Contact > Add Legacy Contact. On a Mac, use System Preferences > Apple ID > Password & Security > Legacy Contact > Manage. You can choose a group member if you’re in a Family Sharing group or pick someone from your contacts list.

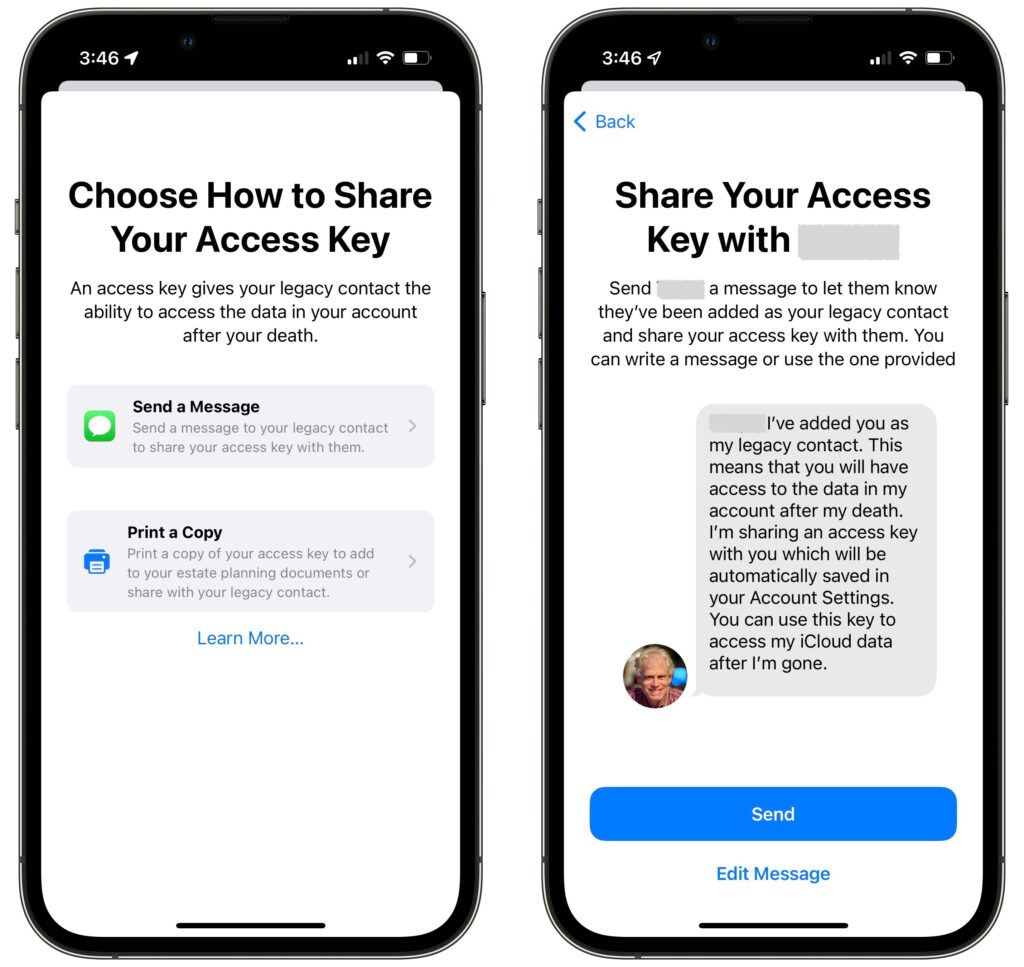
As part of the process of picking someone, Apple allows you to share the access key via Messages if they’re running iOS 15.2, iPadOS 15.2, or macOS 12.1 Monterey. If they accept, a copy of the access key will automatically be stored in their Apple ID settings. If they’re not running a necessary operating system or don’t use an Apple device, you can instead print out an access key QR code and give that to them. You might also want to print a copy to store with your will and other important documents.

It may often be appropriate to act as a Legacy Contact for the people you’re asking to be your Legacy Contacts, particularly with spouses or adult children.
How Does a Legacy Contact Request Account Access?
Let’s assume the worst and pretend that someone who has added you as a Legacy Contact has passed away. To request access to their Apple ID, you need the access key that the person shared with you and a copy of their death certificate. You can find the access key on an iPhone or iPad in Settings > Your Name > Password & Security > Legacy Contact > Contact’s Name, and on the Mac in System Preferences > Apple ID > Password & Security, where you click Manage next to Legacy Contact settings and then Details next to the person’s name. It’s also possible that the person shared the access key as a document stored with their estate planning documents.

The screens that provide the access key also have a Request Access link. Tap or click that and follow the instructions to upload the death certificate. If you don’t have an appropriate Apple device, you can also do this on the Web at Apple’s Digital Legacy – Request Access page.
Apple evaluates all access requests to make sure they’re legitimate, and once approved, sends you an email with more details and instructions. That email will also include a special Legacy Contact Apple ID that replaces the deceased’s previous Apple ID. You can use that Apple ID to log in to iCloud.com or download data at privacy.apple.com, sign in to an Apple device, or restore an iCloud backup to another Apple device. Having an access request approved also removes Activation Lock from the deceased’s Apple devices so you can restore them to factory settings and set them up again, either fresh or with the Legacy Contact’s Apple ID’s data.
The main limitation is that the Legacy Contact Apple ID is good only for 3 years, after which the legacy account is permanently deleted. So be sure to download everything important fairly quickly—don’t just keep using the Legacy Contact Apple ID or assume that you’ll be able to go back to it at any time.
We sincerely hope that you never have to act as Legacy Contact for a loved one, but we can say from experience that this new feature can only help make an already stressful time more manageable.
(Featured image by iStock.com/Olga Serba)
Social Media: Apple’s new Legacy Contact feature makes it simpler for you to give a family member access to your iCloud data after your death. Read on to learn how to make someone a Legacy Contact or what to do if you are a Legacy Contact.