Use Your Apple Watch to Unlock Your Mac, and Apps in Catalina
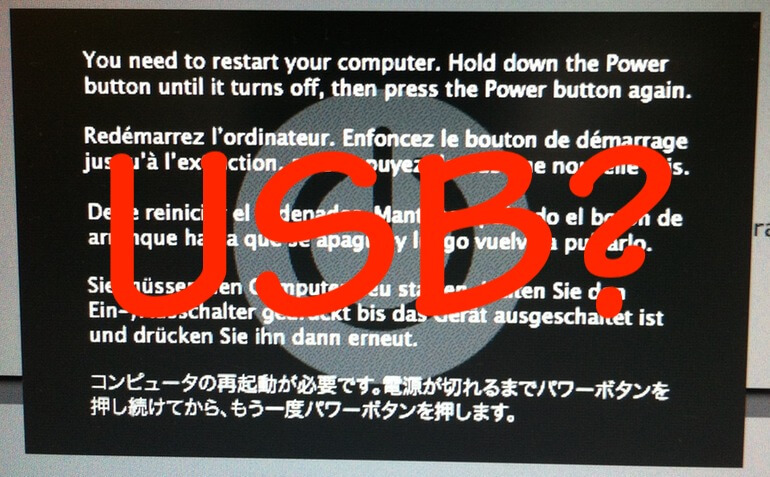
If you’ve resisted requiring a password on your Mac after it wakes up or comes out of the screen saver because it’s too much work to enter repeatedly, an Apple Watch can make authentication much easier. In previous versions of macOS, just wearing an unlocked Apple Watch is enough to enter your Mac’s password; in Catalina, the Apple Watch can also enter your password when prompted by apps. First, make sure your Apple Watch has a passcode (in Watch > Passcode), is on your wrist, and is unlocked. Then, in System Preferences > Security & Privacy > General, select “Use your Apple Watch to unlock apps and your Mac.” From then on, most of the time your Mac or an app wants your password, your Apple Watch will provide it automatically. (This feature requires that the Mac dates from mid-2013 or later, that all devices use the same iCloud account, and that the Apple ID uses two-factor authentication instead of two-step verification.)
(Featured image based on an original by Christin Hume on Unsplash)